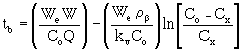|
||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||
The Gerry O. Wood Mathematical Model |
|||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
The Advisor Genius will do this calculation for you. |
|||||||||||||
| How do the results of Wood's Equation compare with Experimental Tests? See the Comparison. | |||||||||||||
| Supporting Data: | |||||||||||||
The parameter We can be estimated using the following equation: |
|||||||||||||
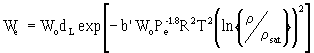 |
|||||||||||||
W o = carbon micropore volume (cm3/g)dL = liquid density of adsorbate (g/cm3) T = absolute temperature (°K = °C + 273) r = partial pressure corresponding to concentration Cx rsat = saturation vapor pressure at temperature T Pe = molar polarization R = ideal gas constant (1.987) b' = an empirical coefficient with value 3.56 x 10-5. The parameter Pe can be estimated using the following equation: |
|||||||||||||
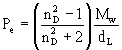 |
|||||||||||||
Mw = molecular weightnD = refractive index The parameter kv has been estimated by Wood from experimental data to be equivalent to the following equation: |
|||||||||||||
I = calculated to be 0.000825S = 0.036 for 1% breakthrough VL = linear airflow velocity (cm/sec) Wood uses an example of hexane with the following information: |
|||||||||||||
T = 22 °C (295 °K).Pair of cartridges with a work rate of 53.3 L/min. Wo = 0.454 [determined from experimental data] dL = 0.6603 [available from scientific handbooks] Pe = 29.877 [calculated from available data] rsat = 121 torr [available from scientific handbooks] r = .38 torr (500 ppm challenge concentration) [calculated from available data] VL = 11.22 cm/s [calculated from available data] W = 70.6 g [calculated from available data] Co = .00178 g/cm3 [calculated from available data] kv = 4242 min-1 |
|||||||||||||
The result of this calculation is: 94 minutes. |
|||||||||||||